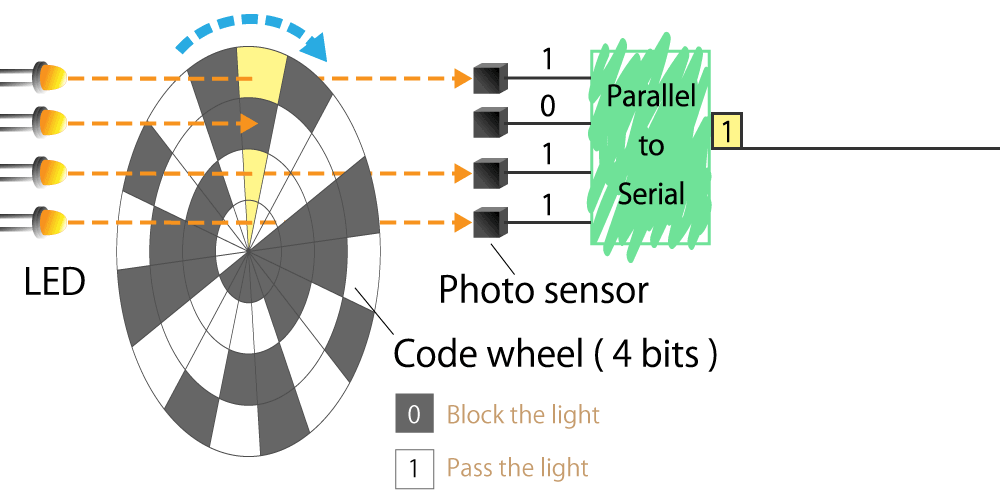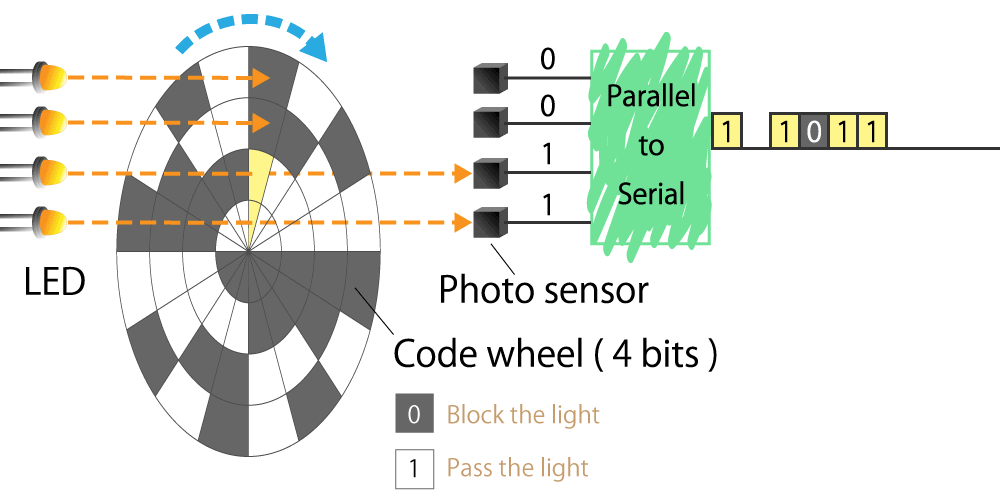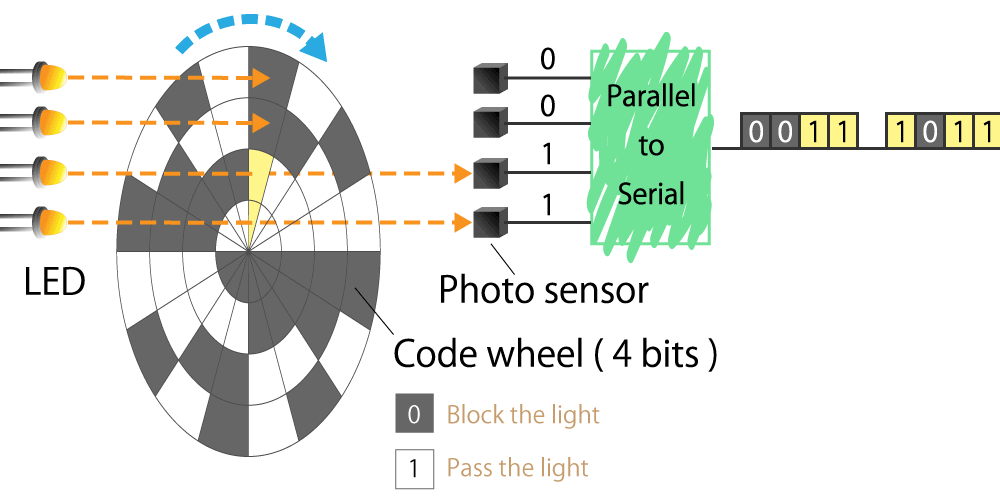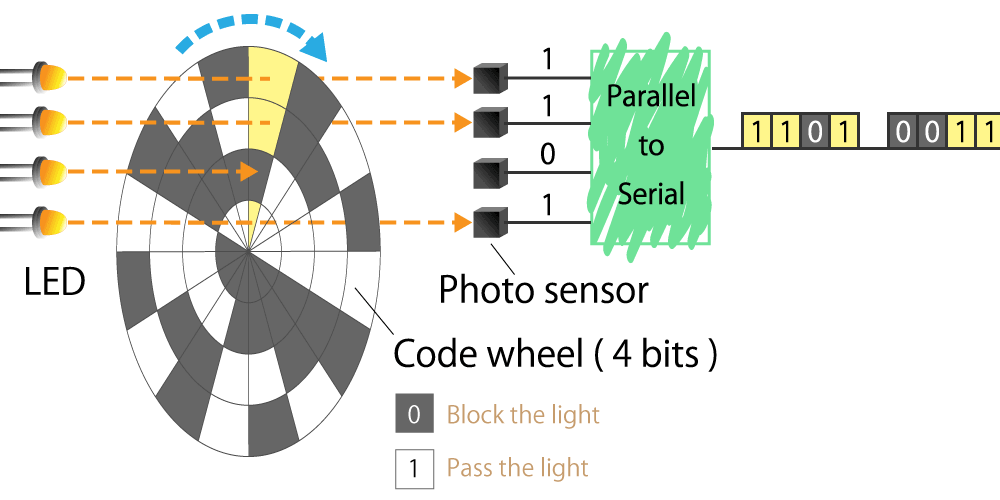
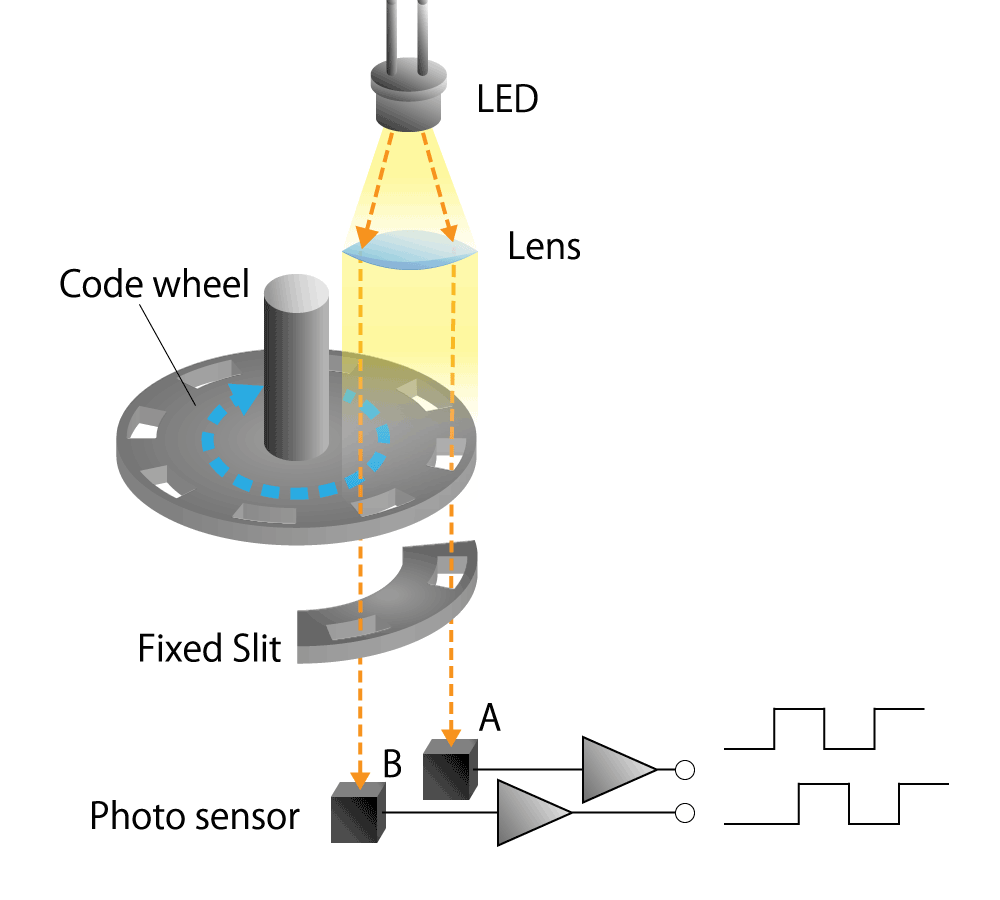
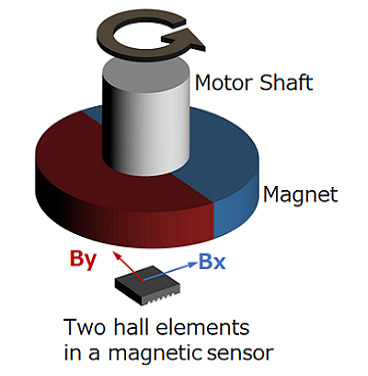
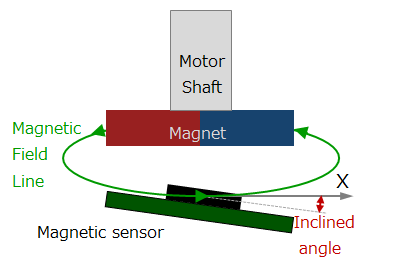
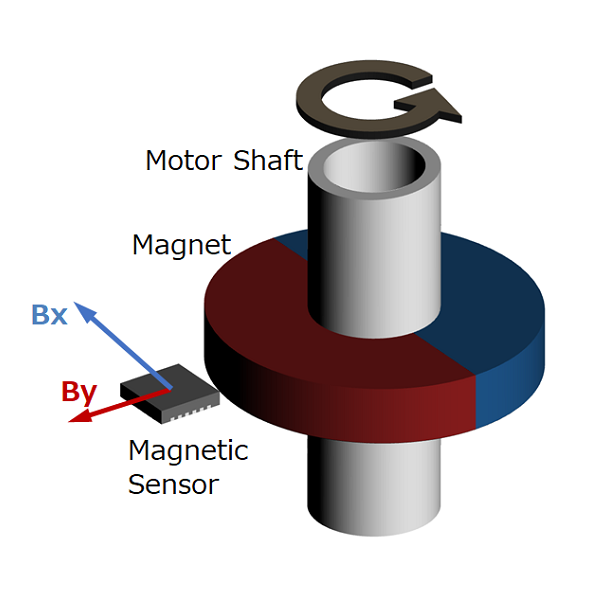
#01
Role of Encoder
Basic Knowledge of Encoder
Those who want to start studying encoders, those who do not deal with encoders but work with those who does.
We hope those people understand what an encoder is.
Summary
- An encoder is a sensor that detects rotation angle or linear displacement.
- Encoders are used in devices that need to operate in high speed and with high accuracy.
- The method of controlling the motor rotation by detecting the motor rotation speed and rotation angle using an encoder is called feedback control (closed loop method).
1-1. How to measure the amount of rotation and rotating speed?
There are various precision instruments around us.
Home Appliances, factory robots and machines... These devices are basically configured as follows.
- Sensors that detect device movement and status
- Controllers that make judgments and process based on signals from sensors
- Actuators that move devices based on information processed by the controllers
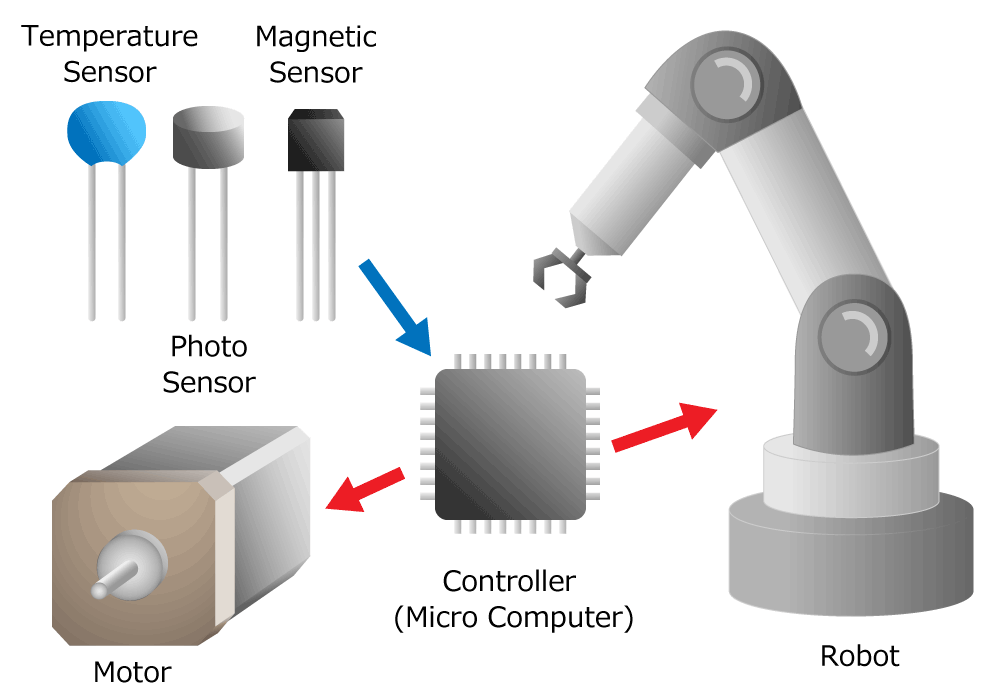 Figure 1. Sensors are essential for moving and controlling various things.
Figure 1. Sensors are essential for moving and controlling various things.
In order to control these devices accurately and quickly, it is essential to detect movements and conditions.
Therefore, electronic components called encoders are used to detect the rotation angle, movement distance, and rotation / movement speed. So what are encoders?
1-2. What is an encoder?
Encoders are sensors that encode rotation angle and linear displacement. An encoder that detects rotation is called a rotary encoder, and an encoder that detects linear displacement is called a linear encoder.
In fact, because the rotary type is used in most cases, when people say simply an encoder, it often refers to a rotary encoder. In this series, we will basically focus on the rotary encoder.
1-3. Where are encoders used?
As mentioned at the beginning, encoders are used in devices that need to operate quickly with high accuracy. Specifically, it is a device that is powered by a motor. For example, encoders are widely used in industrial robots used in factories such as assembly robots, welding robots, automatic guided machines, and machining centers.
However, most people have never seen the latest factory where industrial robots work all the time. Let’s walk through some cases where the encoder is actually used.
Factory automation (Smart factory)
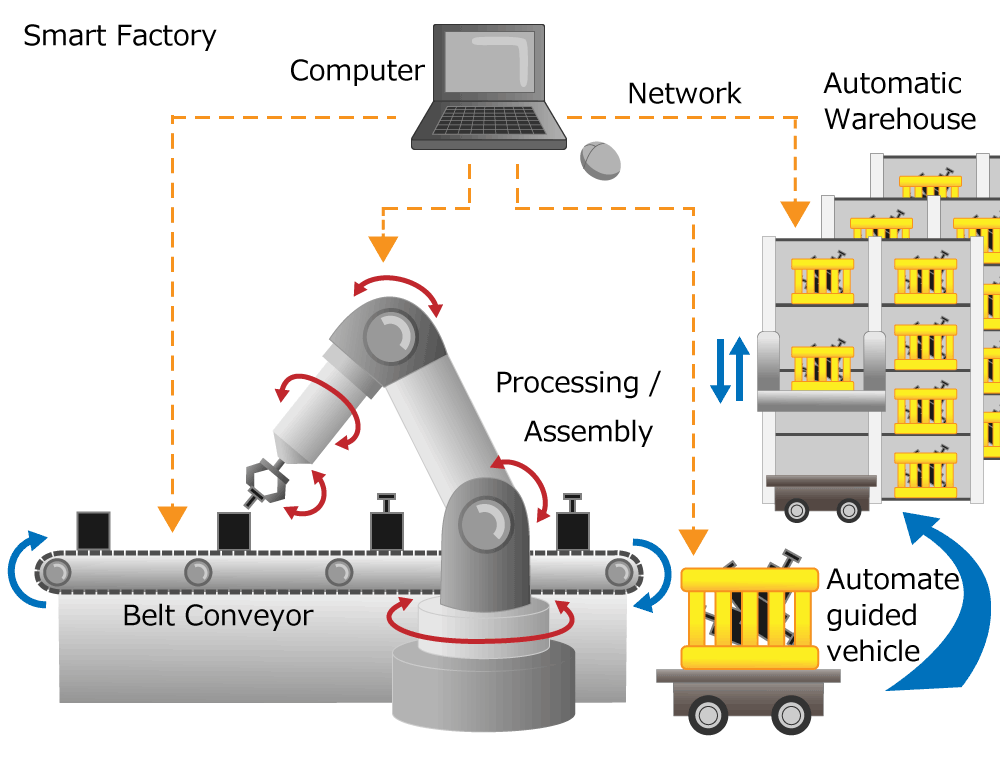 Figure 2. Factory automation (Smart factory)
Figure 2. Factory automation (Smart factory)
Various production facilities are used in factories that produce electrical appliances and automobiles.
A computer controls machine tools that make parts from metal, and a single machine can do various things like cutting flat surfaces, drilling holes, and cutting grooves. Such machine tools are called machining centers.
The produced parts are sent to an assembly factory and automatically assembled by industrial robots such as dedicated assembly machines or arm type robots.
The latest factories are fully automated and using computers and networks for all manufacturing processes of design, part processing, storage, management, transport, and assembly. This concept of “connected factories” is called Industry 4.0, and such factories are called smart factories.
Industrial robots
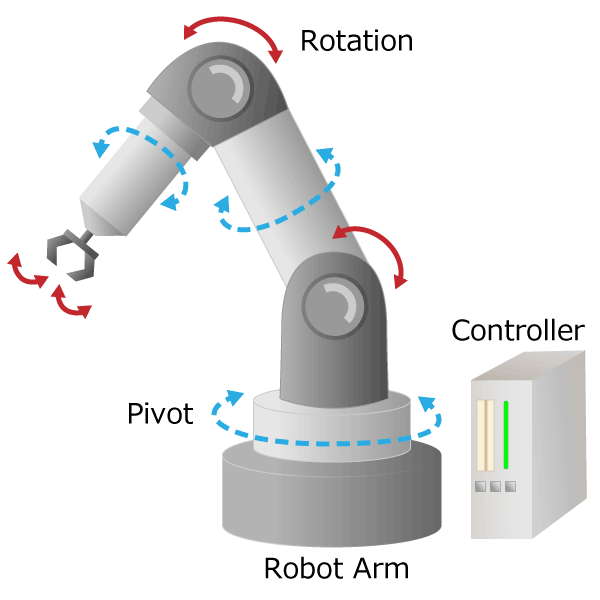
IIndustrial robots free humans from dangerous and demanding work (so-called 3Ds work), increase factory productivity, and stabilize product quality. The most widely used and highly practical industrial robot is an articulated robot with multiple joints equivalent to human shoulders, elbows and wrists. It works like a human arm with pivot, rotation and slide movements. The signal input from the controller is converted into motion by the actuator, and the robot is moved precisely.
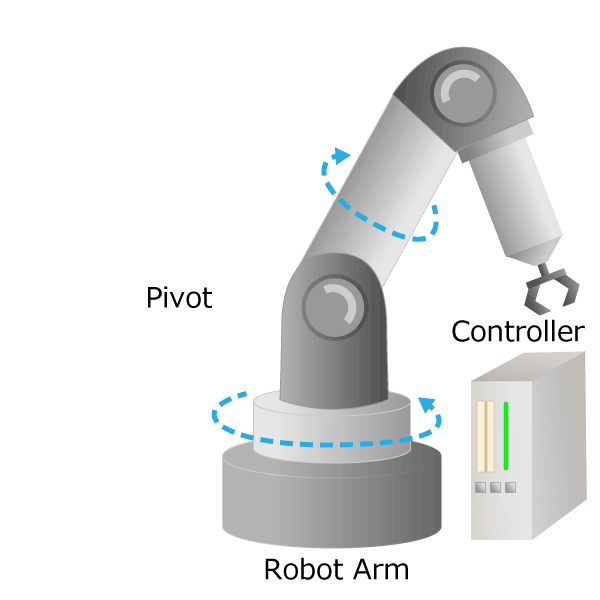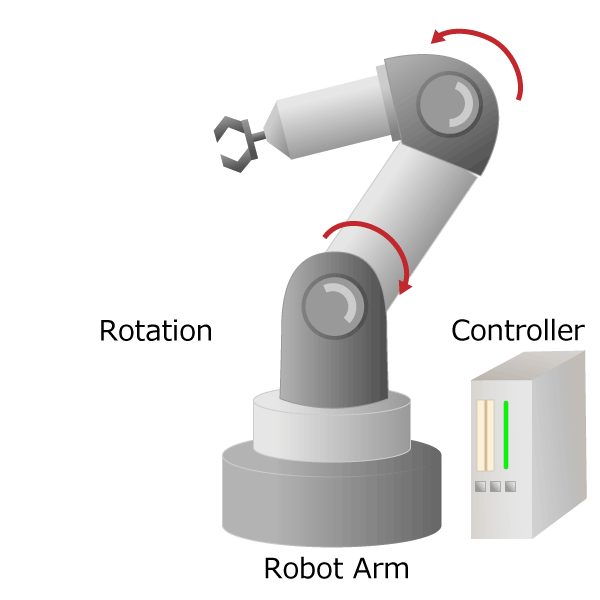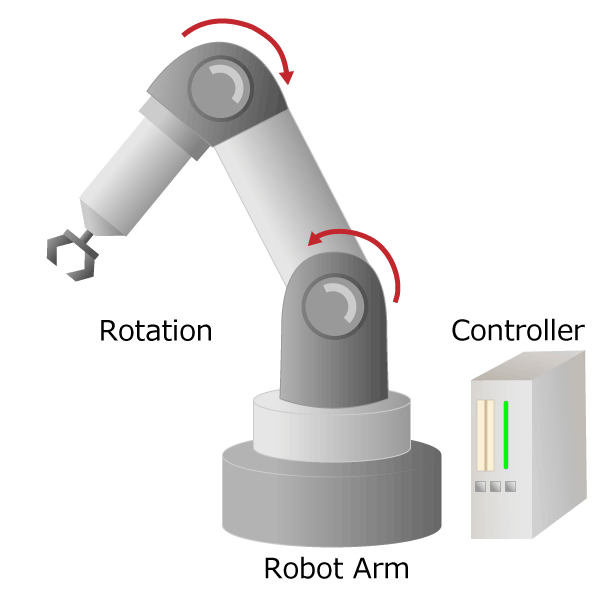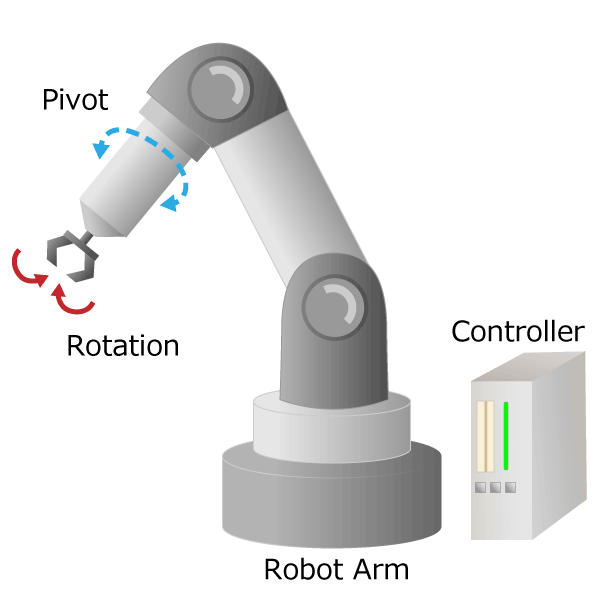 Figure 3. Industrial robot diagram
Figure 3. Industrial robot diagram
The part corresponding to the “arm” from the human shoulder to the wrist is called the manipulator, and the part corresponding to the “hand” form the human wrist to the finger is called the end effector. In industrial robots, by changing the end effector, it is possible to handle not only grabbing but also painting and welding. If you visit a robot or machine tool exhibition, you can actually see the articulated robots on display by various companies.
Actuator
Motors are used as robot actuators because they are easy to miniaturize and have high accuracy. In actual cases, people use actuators with increased rotational force (torque) by integrating a reduction gear that works the same as a bicycle transmission to the output shaft of the motor and slowing down the rotational speed of the motor.
There is also an electric slider that generates a large force in the direction of movement by changing the movement from rotational to linear with a screw.
You can also see these in exhibitions.
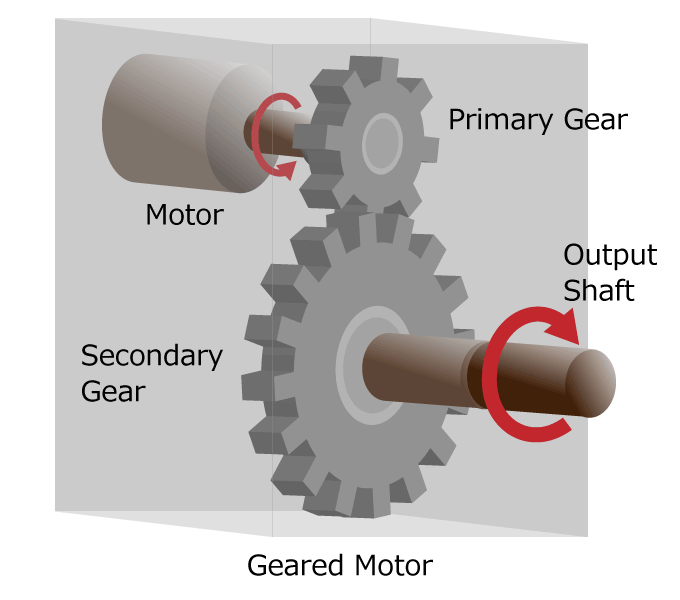 Figure 4a. Geared motor diagram
Figure 4a. Geared motor diagram
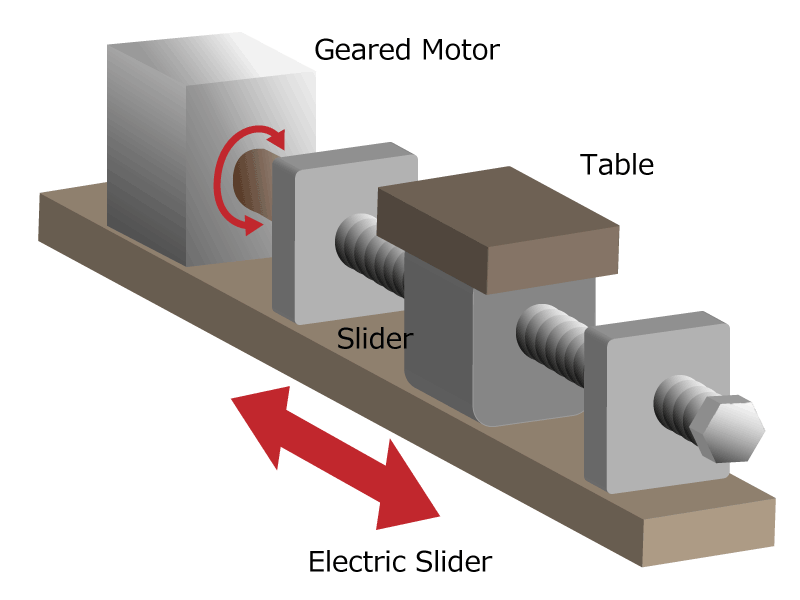 Figure 4b. Electric slider diagram
Figure 4b. Electric slider diagram
Servomotor
There are so many types of motors, and so confusing. We will focus on the motors that use encoders in this article.
One example is a servomotor. The servomotor is the motor that is used in the servomechanism. The servomechanism is the mechanism that keeps the speed of continuous rotational motion or linear motion constant, or precisely controls the rotation angle and travel distance of one movement. The servo motor consists of a brushless DC or AC motor, an encoder, and a servo amplifier (also called a driver).
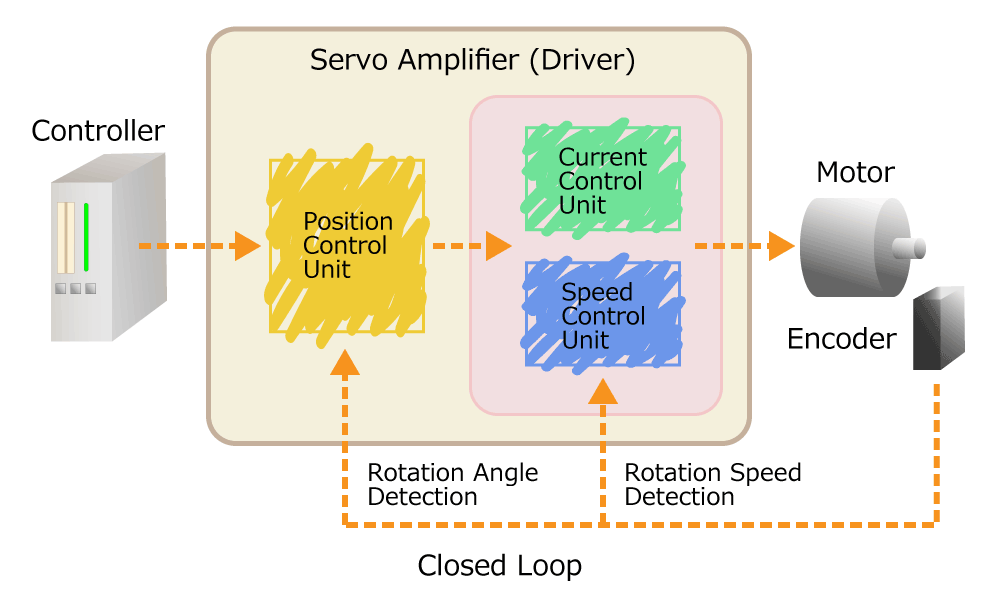 Figure 5. Servo motor diagram
Figure 5. Servo motor diagram
In order to keep the rotation speed of a brushless DC motor or AC motor constant, an encoder detects the rotation speed. The servo amplifier controls to rotate the motor faster if the detected speed is slower than the set rotation speed, or to slower if it is faster.
In order to accurately control the rotation angle of the motor, an encoder detects the rotation angle. The servo amplifier controls the rotation angle of the motor by checking whether it has moved to the target rotation angle.
This method of control by using an encoder to detect the motor rotation speed and rotation angle is called feedback control (closed loop).
Stepper motor
Another is a stepper motor. A stepper motor is a motor that rotates by a certain angle when one pulse signal is input. The stepper motor can be used without feedback (open loop) because the rotation angle and rotation speed are determined by the number of pulse signals applied to the motor and the interval between pulses.
This method has the advantage of simplifying the system because it does not use an encoder. However, the stepper motor has the disadvantage that the efficiency is low. Because it always flows the maximum current to prevent from step-out.
By using the encoder to check whether it is rotating as instructed and feeding back the result, it is not necessary to keep the maximum current, and the power consumption of the system is reduced.
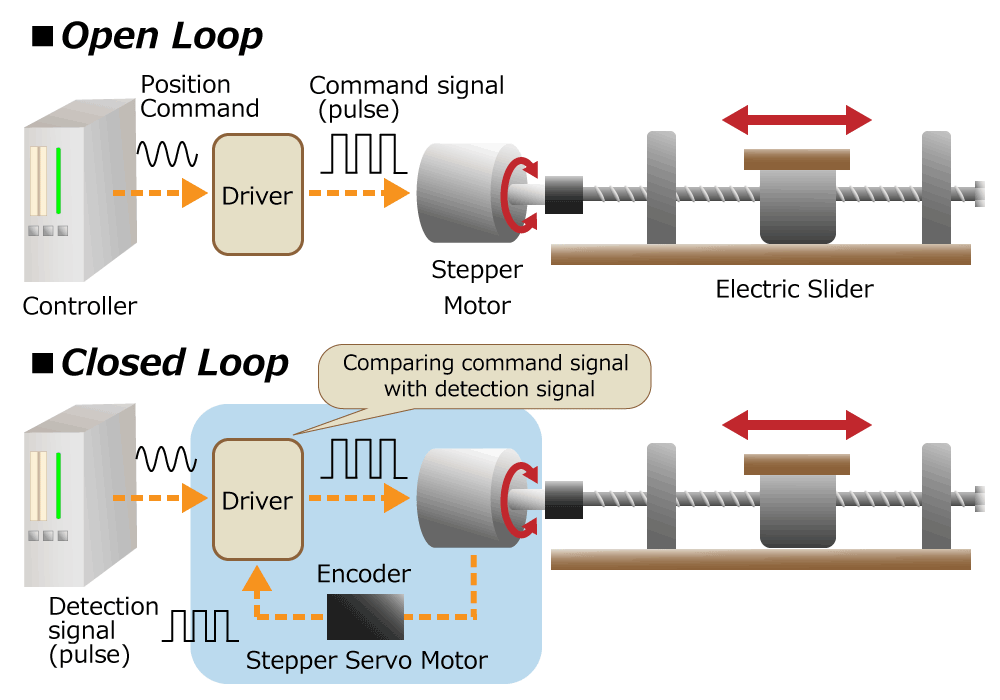 Figure 6. Stepper motor usage
Figure 6. Stepper motor usage
In addition, by checking the load status with an encoder, the operating speed of the actuator can be maximized within the range where the motor does not step-out. This will increase the productivity. Sometimes people call the motor that is used this way the stepper servo motor.
Summary
- An encoder is a sensor that detects rotation angle or linear displacement.
- Encoders are used in devices that need to operate in high speed and with high accuracy.
- The method of controlling the motor rotation by detecting the motor rotation speed and rotation angle using an encoder is called feedback control (closed loop method).
How was it?
In this part, we introduced the role of encoders and where they are used.
I hope you understand the widespread use of encoders.
In the next part, we will explain how the encoder works.
See you again.
Basic Knowledge of Encoder