Types and Characteristics of Current Sensors
Current Sensors
Currently, in many applications including industrial machineries, current sensors have been more used.
For industrial machineries, insulation is often required for current detection, and there are three methods to solve; shunt resistor+isolation amplifier/isolation ADC, cored current sensor, and coreless current sensor (current sensor IC).
In this page, we would like to explain about overview of each method and its advantages/disadvantages.
1. Current measurement methods
The current measurement methods are generally classified by three categories; shunt resistor+isolation amplifier/isolation ADC, cored current sensor, and coreless current sensor (current sensor IC).
The table below shows each method's characteristics. More details focused on each advantage and disadvantage are explained later in this page.
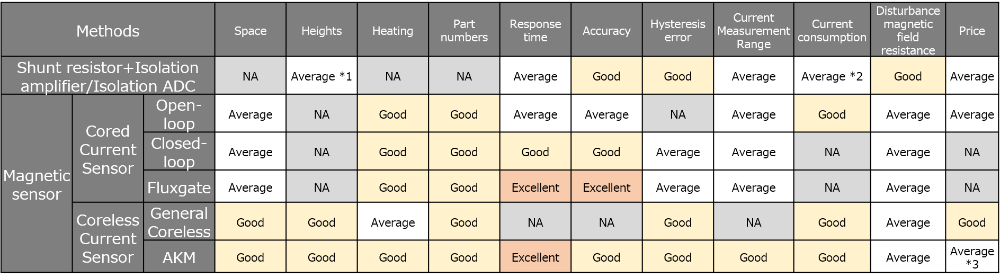 Figure 1. table
Figure 1. table
* 1:If you use cement resistance, it would be changed to "NA".
* 2:Not only on the secondary side but also primary side has current consumption by IC drive.
* 3:If the current is more than 20A, it would be changed to "Good" because of the cost of substrate and fan for radiation of heat.
Points of how to choose proper current measurement method
・Shunt resistor+isolation amplifier/isolation ADC is suitable for the customer who wants to accurately detect microcurrent level (less than 10A) with a large disturbance magnetic field where heat generation is not an issue.
・Fluxgate is suitable for applications which requires the highest accuracy.
・General coreless current sensor is suitable for applications which require small size in small devices and for applications which require lower cost than detecting accuracy.
・AKM's coreless current sensor performs comparable to any other coreless current sensor, as well as cored current sensor(open-loop and closed-loop).
2. Shunt resistor+isolation amplifier/isolation ADC
Shunt resistor+isolation amplifier/isolation ADC is the way to calculate the current value from the voltage value that flows through a known resistor by passing the current to be measured. For this method, it is necessary to be isolated by using isolation amp or isolation ADC.
This method is commonly used and suitable for detecting a small current in a system driven by a relatively low voltage without caring about heat generation.
However, in applications where a large current (more than a few dozen amps) flows, the following disadvantages become apparent.
Advantages
- It is the most well-known way for current detection so that its technology is accumulated in each company.
Disadvantage
- It takes design man-hours because more part numbers, such as insulating power supply and bipolar power supply) are required for the primary side (high voltage side).
- The thermal design is difficult because the heat generated by the primary current is proportional to the resistance and can be several ten times larger compared to other methods.
- The size of the substrate is larger because of the number of peripheral components and complicated wiring.
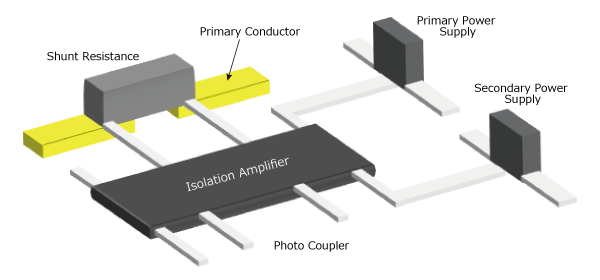 Figure 2. Schematic Diagram of Magnetic Field Generated by Current
Figure 2. Schematic Diagram of Magnetic Field Generated by Current
A magnetic current sensor is a way to solve the disadvantages of above shunt resistor+isolation amplifier/isolation ADC.
3. Magnetic Current Sensor
The principle of the magnetic current sensor is that the current to be measured generates a magnetic field around the current path, and by detecting this generated magnetic field using a magnetic sensor, the amount of the current can be measured.
Magnetic current sensor is different from shunt method, it is no need to use an isolation amp or an isolation ADC because it can be isolated inside the sensor itself.
Since there is no need to change the resistance value depending on the current value, this method is attracting because it can solve the disadvantages of shunt resistor+isolation amplifier/isolation ADC by detecting flowing current to resistors with relatively low resistance values.
3.1. Cored Current Sensor
Cored current sensor is one of the magnetic current sensors. It collects and detects magnetic fields around current lines with magnetic cores.
There are 3 categories for cored current sensor; 1. Open-loop, 2. Closed-loop, and 3. Fluxgate.
Comparison of these 3 categories;
Price: Low Open-loop < Closed-loop < Fluxgate High
Accuracy: Bad Open-loop < Closed-loop < Fluxgate Good
Common Advantages
- The resistance value of the primary conductor is small, so that the heat generation is low.
- Less numbers of parts are needed (No need to use other peripheral parts.)
Common Disadvantages
- Because of the core, there is a difficulty in the space (especially its height).
- The magnetic core theoretically has hysteresis. This can cause the change in zero-current output (offset voltage) and eventually cause the measurement error when the large magnetic field is applied to the core.
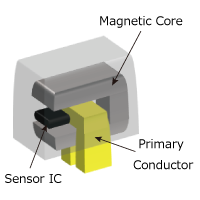 Figure 3. Schematic Diagram of Cored Current Sensors
Figure 3. Schematic Diagram of Cored Current Sensors
The fluxgate method consists of the magnetic core and the probe coil. The probe coil is driven with the high frequency AC and is used as a sensor.
Therefore, it has own advantage that offset hardly occurs in principal regardless of temperature.
However, because of the probe coil, the structure is complicated and it's expensive. In addition, there is a disadvantage that the current consumption increases because of the feedback current.
To remedy above problems, a "coreless current sensor" had been developed.
3-2. Coreless Current Sensor (a current sensor without magnetic core)
Coreless current sensor is a very simple configuration. Magnetic sensor detects the magnetic field created by the measured current flowing through the primary conductor, and IC corrects and amplifies signals from magnetic sensors.
It was developed as a sensor that can solve above cored current sensor's disadvantages while maintaining the advantages. Since the early 2010s, coreless current sensors have been used in many applications that emphasize small size.
3-2-1. General Coreless Current Sensors
General coreless current sensor is integrally construct internal hall element +correction IC with semiconductor silicon in order to achieve small size and low-cost.
Because the sensitivity of silicon hall element is low, it is required to take measures to increase the gain of the correction IC or increase the generated magnetic field by narrowing the primary conductor.
As a result, following advantages and disadvantages have been appeared.
Advantages
- Without magnetic core, it can lower the height. The internal structure can be much simpler so that it can reduce the cost.
- There is no hysteresis.
- Current consumption is low.
Disadvantages
- The resistance value and the heat generation are likely to be higher. It's difficult to measure large current.
- Because sensitivity of the hall element is low, it is desiged to narrow the frequency band to get sufficient resolution. Therefore, the response speed is not so fast.
- It's difficult to achieve high accuracy because increasing the gain of the correction IC also amplifies the offset of the hall element.
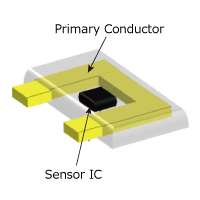 Figure 4. Diagram of a Coreless Current Sensor
Figure 4. Diagram of a Coreless Current Sensor
3-2-2. AKM Coreless Current Sensors
AKM's coreless current sensor has its original technology which can solve above disadvantages of the general coreless current sensors.
Advantages
- Heat generation is low because the primary conductor has low resistance. And it supports a wide measurement current range of ±5 to ±180A.
- By using high sensitive compound semiconductor hall element for sensor, it is high resolution without narrowing the bandwidth.
- Therefore, the bandwidth can be widened and high resolution can be achived.
- It is no need to increase the gain of the correction IC because of the high sensitivity of the hall element, and it's possible to achieve low offset and high accuracy.
Disadvantages
- Compared to general coreless current sensor, Currentier is not cheap.
Recommend
Please refer to the below links for more details about the characteristics of AKM coreless current sensor IC "Currentier".
AKM coreless current sensor IC "Currentier"
Small package and system downsizing by low-heat generation
Board commonality with wide current measurement range and simplification of thermal design by low-heat generation
Standards of insulation (UL compliant/certified) and over current detection function
System efficiency by accuracy, low noise characteristics, and good temperature characteristic